Planning Your Winter Garden: From Frost to Feast

As the temperatures drop and the days grow shorter, many gardeners hang up their gloves and trowels, assuming that gardening is reserved for warmer seasons. However, with proper planning and preparation, a winter garden can flourish, providing fresh produce even in the coldest months.
In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the steps to plan and cultivate a successful winter garden. From assessing your garden and climate to choosing the right winter crops, and from planning and timing your winter planting to preparing the soil and implementing seasonal protection measures, we will cover it all.
Winter gardening presents unique challenges, but with the right strategies, you can extend the growing season and enjoy the rewards of your efforts. Imagine stepping into your garden in the midst of winter and harvesting vibrant greens, crisp root vegetables, and fragrant herbs that will elevate your winter meals.
Whether you're a seasoned gardener looking to expand your growing season or a beginner eager to embark on a new gardening adventure, this guide will provide you with valuable insights and practical tips for planning your winter garden. Get ready to transform your garden into a winter wonderland of fresh and flavourful delights.
Let's dive in and explore the world of winter gardening, where frost turns into feast!
Understanding the Benefits of Winter Gardening
Winter gardening offers numerous advantages, making it a rewarding endeavour for green thumbs seeking year-round enjoyment and fresh produce. By comprehending the benefits associated with winter gardening, you can gain a deeper appreciation for this unique gardening practice and make the most of your winter garden. Consider the following points:
1. Exploring the advantages of growing a winter garden
Winter gardening presents an array of benefits that set it apart from traditional gardening during warmer seasons. These advantages include:
- Extended harvest season: With a well-planned winter garden, you can continue harvesting fresh vegetables, fruits, and herbs even when outdoor conditions are frosty.
- Access to fresh, nutritious produce: By growing your own winter crops, you can enjoy a bountiful supply of organic, nutrient-rich food, ensuring a healthy diet throughout the winter months.
- Cost savings: Homegrown winter produce reduces reliance on store-bought options, potentially leading to significant savings on grocery bills.
- Increased self-sufficiency: Winter gardening allows you to become more self-reliant by cultivating your own food supply, regardless of the season.
- Year-round gardening practice: Engaging in winter gardening expands your gardening skills and knowledge, providing a year-round connection to nature and the joy of cultivation.
2. Enjoying fresh produce during the colder months
Winter gardens offer the opportunity to savour the flavours of fresh, homegrown produce even when the outdoor environment seems inhospitable. Imagine plucking vibrant, crisp greens, robust root vegetables, and fragrant herbs right from your garden, elevating your winter meals with a farm-to-table experience.
3. Enhancing your gardening skills and knowledge
Winter gardening challenges you to adapt to specific conditions and learn new techniques, helping you grow as a gardener. It expands your understanding of cold-hardy crops, frost protection methods, and strategies for maximising yields in less favourable weather. With each winter gardening season, you'll gain valuable insights and develop a more resilient and diverse set of gardening skills.
By recognizing and embracing the benefits of winter gardening, you can embark on a rewarding journey of planning and cultivating a winter garden that not only sustains you with fresh produce but also enriches your gardening expertise and enjoyment throughout the year.
Assessing Your Garden and Climate
After understanding the benefits of winter gardening, the next crucial step is to assess your garden and climate to determine the feasibility of a successful winter garden. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make informed decisions and create an optimal environment for your winter crops. Consider the following steps:
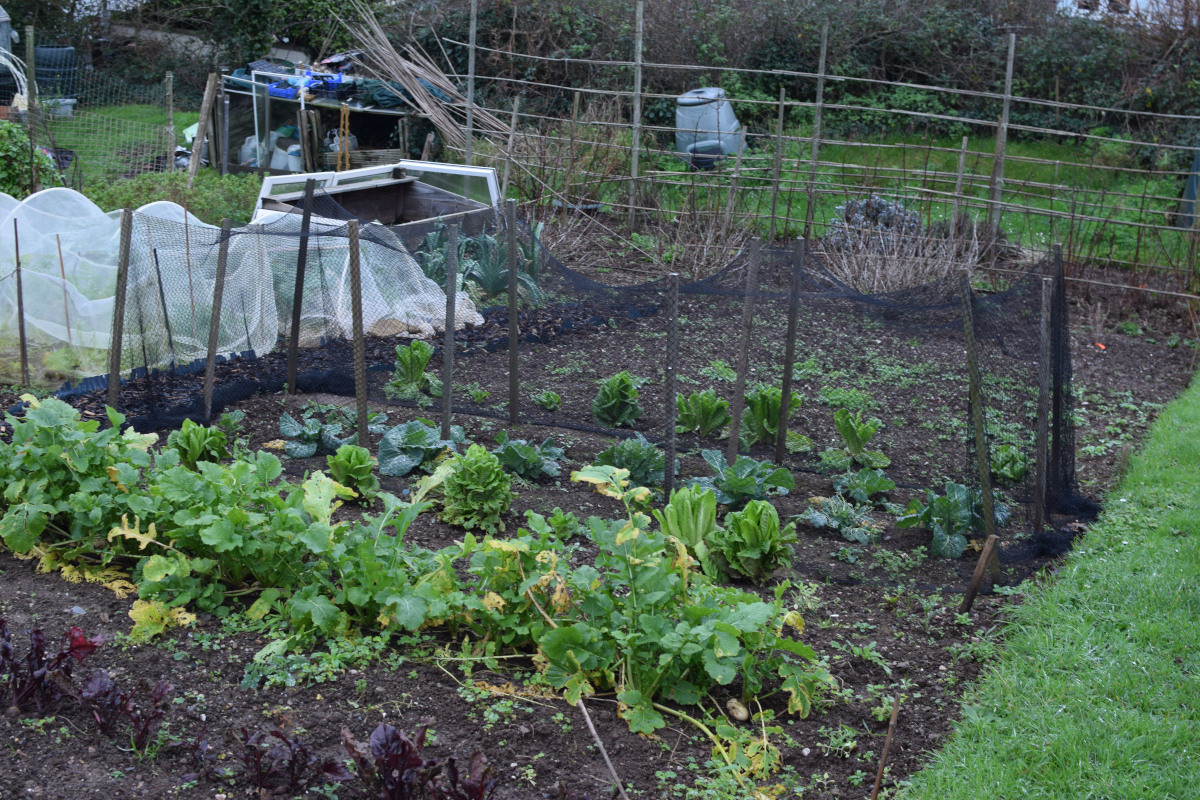

1. Evaluating your garden space for winter gardening potential
Start by assessing the characteristics of your garden space to determine its suitability for winter gardening:
- Sunlight exposure: Observe the areas of your garden that receive the most sunlight during the winter months. Identify spots with at least 6 hours of direct or indirect sunlight, as this is crucial for the growth of winter crops.
- Microclimates: Pay attention to microclimates within your garden, such as areas sheltered from wind or near heat-retaining structures like walls or fences. These microclimates can provide additional protection for delicate plants during the winter.
2. Researching your local climate and frost dates
Understanding your local climate and frost dates is essential for successful winter gardening. Research the following information specific to your region:
- Average winter temperatures: Determine the average low temperatures during winter to assess the severity of cold conditions your plants may face.
- Frost dates: Identify the first and last expected frost dates in your area. This information helps you plan planting and harvesting schedules.
3. Selecting suitable winter crops based on your region
Based on your garden space and local climate, choose winter crops that thrive in your specific conditions:
- Cold-hardy vegetables: Look for vegetables such as kale, spinach, Swiss chard, Brussels sprouts, carrots, radishes, and winter squash, which can withstand colder temperatures.
- Winter-adapted varieties: Opt for specific varieties of vegetables and fruits that are known to perform well in winter conditions. These varieties are often labelled as suitable for winter or cold climates.
- Perennial herbs: Consider incorporating perennial herbs like rosemary, thyme, sage, and chives, which can survive and even thrive during winter.
By assessing your garden space and understanding your local climate, you can make informed decisions about the types of winter crops to grow and create an environment that maximises their chances of success. This evaluation sets the stage for the next step: selecting the right winter crops and planning their planting and care.
Choosing the Right Winter Crops
When planning your winter garden, it's important to select the right crops that can thrive in your specific climate and garden conditions. Different regions and climates offer varying opportunities for winter gardening. Consider the following steps to choose the most suitable winter crops for your garden:
1. Researching winter crops for your specific climate
Each climate zone has its own set of winter crops that perform well in those conditions. Research and identify the winter crops recommended for your particular climate zone. Keep in mind that what grows well in one region may not be suitable for another.
2. Identifying cold-hardy vegetables and fruits
Look for cold-hardy vegetables and fruits that can withstand freezing temperatures and continue to grow during the winter months. Examples of cold-hardy vegetables include kale, collard greens, spinach, Brussels sprouts, and winter squash. Fruits such as winter varieties of apples and pears can also thrive in colder climates.
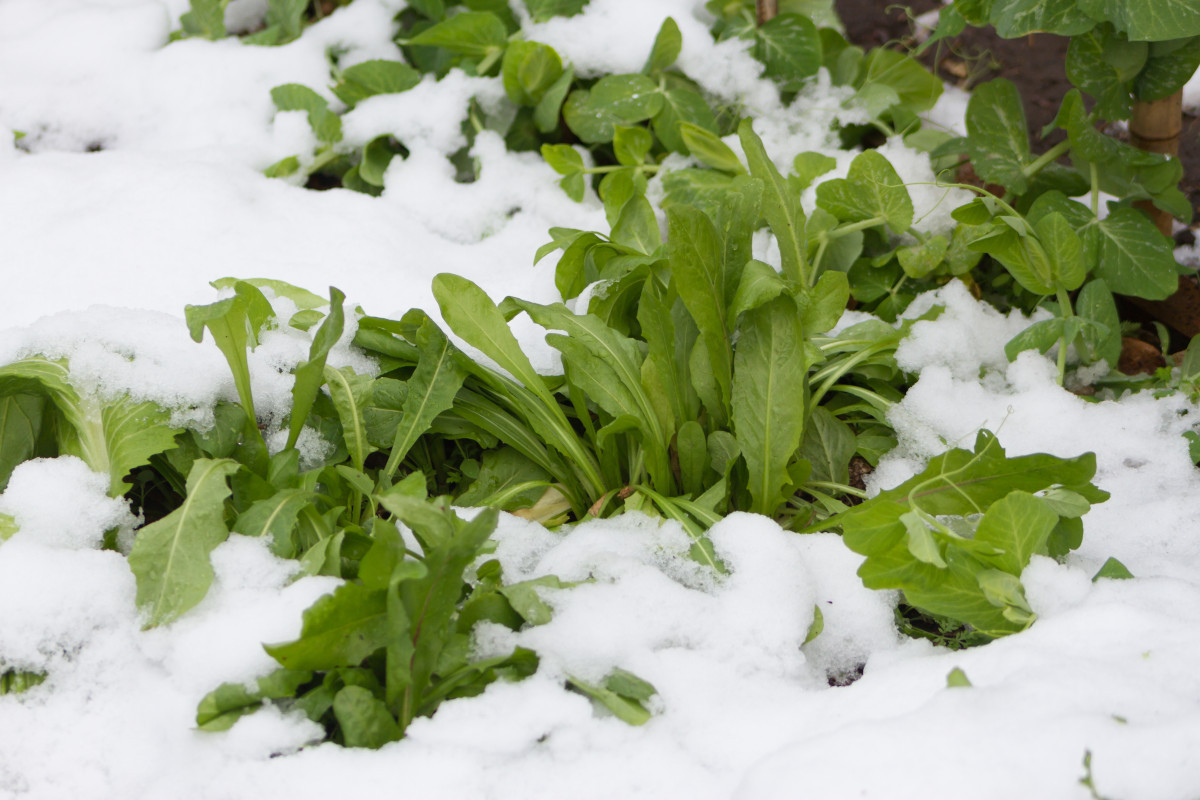

3. Considering winter-adapted varieties
Some plant varieties are specifically bred or adapted to thrive in winter conditions. These varieties have characteristics that enable them to withstand colder temperatures, resist diseases, and continue growing with limited daylight. Look for winter-adapted varieties of popular vegetables like lettuce, radishes, carrots, and broccoli.
4. Incorporating perennial herbs for year-round harvests
Perennial herbs are an excellent addition to a winter garden, as they can provide fresh flavors and aromas all year round. Consider growing herbs like rosemary, thyme, sage, and chives, which are known to be hardy and can withstand winter temperatures.
It's essential to note that the available winter crops may vary depending on your specific climate. Some regions with mild winters may have a broader selection of crops to choose from, while colder climates might have a more limited range of options. Adapt your crop selection to suit the unique conditions of your garden and climate.
By carefully selecting winter crops that are suitable for your specific climate and garden conditions, you can ensure a successful and productive winter garden. These crops will be better equipped to thrive and provide you with fresh, homegrown produce throughout the winter season.
We have another article that lists the TOP 10 WINTER VEGETABLES TO GROW
Planning and Timing Your Winter Planting
Effective planning and timing are crucial for a successful winter garden. By carefully considering planting schedules, succession planting, and utilizing helpful tools like vegetable garden planning software, you can optimize your winter planting. Follow these steps to plan and time your winter planting:
1. Determining the ideal planting dates
Research and determine the ideal planting dates for each winter crop you have chosen. These dates are typically based on the expected first frost date and the crop's specific growing requirements. Consider the recommended planting guidelines for your region to ensure that your crops have enough time to mature before the coldest part of winter.
2. Implementing succession planting
Succession planting involves staggering your plantings to ensure a continuous supply of winter crops. Instead of planting all your crops at once, sow seeds or transplant seedlings at intervals, typically every 2-3 weeks. This approach allows for a more extended harvest period and reduces the risk of overwhelming yields or crop wastage.
3. Utilizing vegetable garden planning software
Vegetable garden planning software, such as vegplotter.com, can be a valuable tool in organizing and optimizing your winter garden. These tools often provide features like drag-and-drop functionality, crop rotation planning, and customizable planting schedules. By utilizing such software, you can visualize your garden layout, plan your plantings, and manage your crops more efficiently.
Note: Vegetable garden planning software like vegplotter.com can assist you in maximizing your garden's potential, ensuring optimal space utilization, and helping you keep track of planting and harvesting dates. These tools can save time and effort by streamlining the planning process and providing valuable insights into your winter garden.
4. Considering frost protection measures
Winter crops require protection from frost and cold temperatures. Consider employing various frost protection measures such as row covers, cloches, cold frames, or hoop houses. These structures provide insulation and shield plants from freezing temperatures, extending the growing season and protecting delicate crops.
By carefully planning your winter planting, implementing succession planting, utilizing vegetable garden planning software, and implementing frost protection measures, you can optimize your winter garden for maximum yields and success. A well-executed plan ensures that your crops are timed appropriately, and you can enjoy a steady supply of fresh produce throughout the winter months.
Preparing the Soil for Winter Planting
To ensure healthy plant growth and abundant yields in your winter garden, it's essential to prepare the soil properly. Preparing the soil before winter planting sets the foundation for optimal nutrient availability, drainage, and root development. Follow these steps to prepare your soil for winter planting:
1. Clearing debris and weeds
Begin by removing any debris, old plant residues, and weeds from the garden bed. These can harbor pests, diseases, and compete for nutrients with your winter crops. Clearing the bed creates a clean slate for your new plantings.
2. Amending the soil with organic matter
Enhance the soil's fertility and structure by incorporating organic matter such as compost, well-rotted manure, or leaf mold. Organic matter improves soil drainage, moisture retention, and nutrient levels, creating an ideal environment for plant growth. Spread a layer of organic matter over the bed and work it into the soil using a garden fork or tiller.
3. Testing and adjusting soil pH
Conduct a soil test to determine the pH level of your soil. Most winter crops thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6.0-7.0). If the pH is outside the desired range, you can adjust it by adding soil amendments like lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it. Follow the recommendations from your soil test results or consult a local agricultural extension office for guidance.
4. Providing balanced nutrients
Ensure your winter crops have access to essential nutrients by applying a balanced organic fertilizer or a winter-specific fertilizer. These fertilizers typically contain a mix of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with trace minerals. Follow the fertilizer's instructions for application rates and methods, keeping in mind the specific nutrient requirements of your chosen winter crops.
5. Improving soil structure
Enhance the soil's structure by incorporating organic matter and loosening compacted areas. This improves root penetration, water infiltration, and nutrient uptake. Use a garden fork or a tiller to gently loosen the soil, being careful not to disrupt the soil layers excessively.
6. Mulching the garden bed
Apply a layer of mulch, such as straw, wood chips, or shredded leaves, to the garden bed. Mulch helps regulate soil temperature, retain moisture, suppress weeds, and prevent soil erosion. Spread a 2-3 inch layer of mulch over the soil surface, keeping it a few inches away from the plant stems to prevent rotting.
By preparing the soil adequately before winter planting, you provide your crops with a healthy growing environment. The amended soil will retain moisture, provide essential nutrients, and support robust root development, ensuring that your winter garden thrives throughout the season.
Implementing Seasonal Protection Measures
Protecting your winter garden from harsh weather conditions is crucial to ensure the survival and productivity of your crops. Implementing seasonal protection measures can help safeguard your plants from frost, wind, and other winter challenges. Consider the following steps to protect your winter garden:
1. Installing row covers and cloches
Row covers and cloches create a protective barrier around your plants, shielding them from frost, wind, and temperature fluctuations. Floating row covers made of lightweight fabric allow sunlight, air, and water to reach the plants while providing insulation. Cloches, on the other hand, are individual coverings that protect individual plants or small sections of the garden.
2. Building cold frames or hoop houses
Cold frames and hoop houses are structures that provide additional protection to your winter crops. They capture solar heat during the day and create a warmer microclimate, extending the growing season. Cold frames have a transparent top, usually made of glass or plastic, while hoop houses are constructed with a series of hoops covered with a plastic film.
3. Using mulch for insulation
Mulching your garden beds with a layer of organic mulch helps insulate the soil and protect the plant roots from extreme temperatures. Mulch acts as a barrier, reducing heat loss from the soil and preventing rapid freezing and thawing cycles. Apply a thick layer of mulch, such as straw or shredded leaves, around the base of your plants, ensuring they are not smothered.
4. Providing windbreaks
Strong winter winds can damage or uproot your plants. To protect them, create windbreaks using structures like fences, trellises, or hedges. These barriers help redirect or block the wind, reducing its impact on your garden. Position windbreaks on the side of prevailing winds for maximum effectiveness.
5. Monitoring and adjusting watering
During winter, plants require less water due to reduced evaporation rates and slower growth. Monitor soil moisture levels regularly and adjust your watering accordingly. Avoid overwatering, as excess moisture can lead to root rot in cold and wet conditions. Water your plants during the warmest parts of the day to prevent freezing overnight.
6. Inspecting for pests and diseases
Even in winter, pests and diseases can affect your plants. Regularly inspect your garden for signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate action. Remove any infected or damaged plant material promptly to prevent the spread of diseases. Consider using organic pest control methods or beneficial insects to manage pest populations.
By implementing these seasonal protection measures, you can safeguard your winter garden from adverse weather conditions, ensuring the health and productivity of your crops. These measures create a more favorable environment, allowing your plants to thrive and provide you with a bountiful harvest throughout the winter season.
Harvesting and Enjoying Your Winter Produce
After careful planning, preparation, and nurturing, it's time to reap the rewards of your winter garden. Harvesting your winter produce at the right time ensures peak flavor, freshness, and nutritional value. Follow these tips to harvest and enjoy the fruits of your labor:
1. Monitor maturity and readiness
Regularly monitor your crops to determine their maturity and readiness for harvest. Different crops have specific indicators of ripeness, such as color changes, size, or firmness. Refer to seed packets or gardening resources for guidance on identifying the optimal harvest time for each crop.
2. Harvest in favorable conditions
Choose a dry day with mild temperatures to harvest your winter produce. Wet conditions can lead to rotting or mold development, while freezing temperatures can damage delicate crops. Harvest in the morning when the plants are hydrated but have not been exposed to direct sunlight for an extended period.
3. Use proper harvesting techniques
Gently harvest your winter crops using appropriate techniques to avoid damaging the plants. Use clean, sharp garden scissors or pruners to cut leafy greens just above the soil level. For root crops, carefully loosen the soil around the base and lift them out. Be mindful not to bruise or break the harvested produce.
4. Handle and store harvested crops properly
Handle your harvested crops with care to prevent bruising or other damage. Remove any excess dirt or debris, and gently wash the produce if necessary. Store leafy greens and herbs in the refrigerator, preferably wrapped in a damp paper towel or stored in a plastic bag to maintain freshness. Root vegetables can be stored in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated area.
5. Enjoy the flavors of winter
Once harvested, it's time to savor the flavors of your winter produce. Incorporate your homegrown vegetables and fruits into delicious winter recipes, such as hearty soups, roasted vegetables, or warming stews. The freshness and quality of your homegrown produce will enhance the taste of your culinary creations.
6. Reflect and plan for future seasons
Take the time to reflect on your winter gardening experience. Note which crops performed exceptionally well and which ones could be improved in future seasons. Consider keeping a gardening journal to record your observations and learnings. Use this knowledge to refine your winter gardening plans for the following year and continually enhance your skills as a gardener.
By harvesting and enjoying your winter produce, you can fully appreciate the rewards of your hard work and dedication. Delight in the fresh flavors and nutritional benefits of your homegrown crops while gaining valuable insights for future gardening endeavors.
Conclusion
Planning and cultivating a winter garden is a rewarding endeavor that allows you to enjoy fresh produce even during the colder months. By following a few key steps, you can create a thriving winter garden that provides an abundance of nutritious crops.
Start by assessing your garden and climate to understand the specific challenges and opportunities for winter gardening in your region. Consider the frost dates, sunlight exposure, and microclimates within your garden space.
Next, choose the right winter crops that are suitable for your climate and garden conditions. Keep in mind that different regions will have different plants that thrive in winter, so select varieties that are known to perform well in your area.
Once you've selected your crops, plan and time your winter planting carefully. Use resources like vegetable garden planning software to visualize your garden layout, manage planting schedules, and optimize space utilization. Consider implementing succession planting to ensure a continuous supply of fresh produce throughout the season.
Preparing the soil is essential for the success of your winter garden. Clear away debris and weeds, amend the soil with organic matter, and adjust the pH levels if necessary. Improving soil structure and providing balanced nutrients create a healthy growing environment for your crops.
Implementing seasonal protection measures safeguards your plants from frost, wind, and temperature fluctuations. Use row covers, cloches, cold frames, or hoop houses to create a sheltered environment. Apply mulch for insulation, create windbreaks, and monitor watering needs to keep your plants healthy.
Finally, when the time comes, harvest your winter produce at its peak ripeness. Handle and store your crops properly to maintain their freshness and taste. Enjoy the flavors of winter by incorporating your homegrown produce into delicious meals and reflect on your gardening experience to improve future seasons.
With careful planning, preparation, and nurturing, your winter garden can provide a bountiful harvest and a source of pride. Embrace the joys of growing your own food and relish the flavors of winter with homegrown goodness.
Happy winter gardening!