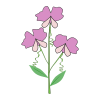
Sweet peas, scientifically known as Lathyrus odoratus, are beloved for their delicate, butterfly-like blossoms and enchanting fragrance. Originating from the Mediterranean region, these annual climbing plants have become popular in gardens worldwide. Sweet peas thrive in cool climates and bloom predominantly in early summer, offering a colorful display of flowers that range from white and pink to deep purples and vibrant reds.
The flowers of sweet peas are not only visually striking but also highly aromatic, making them a favorite for cut flower arrangements and perfumes. Each bloom gracefully balances on slender, tendril-clad stems, creating a soft and romantic appearance. The plant can grow up to six feet tall when supported by trellises or other structures, allowing it to create lush vertical displays in garden spaces.
Cultivation of sweet peas requires well-drained soil, moderate watering, and plenty of sunlight. They are often grown from seed and can be sown directly into the ground in early spring. Gardeners typically pinch back the young plants to encourage bushier growth and more abundant flowering.
In addition to their aesthetic appeal, sweet peas have a symbolic significance, often representing delicate pleasure, departure, or blissful pleasure in the language of flowers. Their enduring popularity in gardens and floral arrangements underscores their beauty and the joy they bring to those who grow and admire them.
How To Grow
Growing sweet peas is a rewarding endeavor for any gardener looking to add vibrant color and delightful fragrance to their garden. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to grow sweet peas from seed:
-
Choose the Right Variety
Start by selecting a variety of sweet pea that suits your climate and the color scheme of your garden. There are many varieties available, ranging from climbing types that are perfect for trellises to bush types suitable for containers.
-
Timing for Planting
Sweet peas thrive in cool temperatures, so the best planting time depends on your local climate. In cooler regions, sow seeds outdoors as early as possible in spring, once the soil can be worked. In warmer areas, consider planting in late fall for winter blooms.
-
Prepare the Soil
Choose a sunny site with well-draining soil. Sweet peas prefer a neutral to slightly alkaline pH. Enrich the soil with compost or well-rotted manure before planting to improve fertility and drainage.
-
Seed Preparation
Sweet pea seeds have a hard outer coating, so it’s beneficial to soften them to enhance germination. You can do this by soaking the seeds in water for 24 hours or gently nicking the seed coat with a file.
-
Sowing Seeds
Plant seeds about 1 inch deep and 2-3 inches apart. If planting in rows, space the rows about 18 inches apart. Cover the seeds with soil, pat down gently, and water well.
-
Support Structures
If you are growing climbing varieties, provide support such as a trellis, netting, or stakes at planting time to encourage vertical growth.
-
Care and Maintenance
Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. Water at the base of the plants to avoid wetting the foliage, which can lead to fungal diseases.
Once seedlings are a few inches tall, thin them to about 6 inches apart to allow adequate air circulation and room for growth.
Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer when plants are 4-6 inches tall and again when they begin to bloom.
-
Pinching Out
When plants have 3-4 pairs of leaves, pinch out the central growing tip just above a set of leaves to encourage bushy growth and more flowers.
-
Pest and Disease Management
Watch for common pests like aphids and slugs. Use environmentally friendly methods such as hand-picking pests off plants, using barriers for slugs, and spraying aphids with water or insecticidal soap.
Avoid overcrowding and wet conditions to minimize the risk of fungal diseases.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to enjoy the beautiful sights and smells of sweet peas throughout their growing season. Whether climbing on a trellis or flourishing in a pot, sweet peas make a lovely addition to any garden.
How/When To Harvesting
Harvesting sweet peas properly can extend their blooming season and enhance your enjoyment of these beautifully scented flowers. Here's how to harvest sweet peas effectively:
-
Timing
The best time to pick sweet pea flowers is in the morning when the flowers are freshly opened and the temperatures are still cool. This ensures the flowers are at their most fragrant and have a higher moisture content, which helps them last longer after cutting.
-
Choosing Flowers to Cut
Look for flowers that have just opened or are about to open. You’ll typically find that each stem has several buds at different stages of opening. Choose stems with at least one or two open flowers and a few unopened buds.
-
Cutting Technique
Use sharp scissors or pruning shears to make clean cuts. Cut the stem above a leaf joint, and try to leave at least two to three leaves on the stem remaining on the plant. This helps the plant to continue growing healthily and produce more blooms.
-
Length of Stems
When cutting the stems, aim for a length that suits your vase or intended use. Longer stems are usually more versatile for floral arrangements. However, ensure you do not strip the plant too bare; leave enough foliage to sustain the plant's health.
-
Post-Harvest Care
Immediately after cutting, place the stems in a bucket of cool water. Keeping them in water from the moment they are cut helps prevent them from wilting.
-
Conditioning
Before arranging them in a vase, re-cut the stems underwater to avoid air embolisms that can block water uptake. Remove any leaves that will be below the waterline in your vase to prevent bacterial growth.
-
Arrangement and Display
Arrange the sweet peas in a clean vase filled with fresh water mixed with a floral preservative. This will help extend the life of your flowers. Change the water and trim the stems slightly every few days to keep the flowers fresh.
-
Regular Harvesting
Regularly harvesting sweet peas encourages the plant to produce more flowers. Try to harvest every few days to prevent the flowers from going to seed, as seed formation signals the plant to stop flowering.
-
End of Season Care
As the season ends and fewer flowers are produced, you can allow some pods to mature and collect the seeds for next year if you wish. However, remember that many modern cultivars do not produce viable seeds, or the seeds may not grow true to the parent plant.
By following these steps, you can enjoy vibrant and fragrant sweet peas throughout their growing season, and using them in bouquets will brighten your home and give you a wonderful, natural fragrance.